A hip replacement is a common type of surgery where a damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial one (known as prosthesis).
A hip replacement is a very common procedure. Just over 70,000 hip replacements in carried out in the United Kingdom each year. Waiting lists in many Trusts are 18 weeks and some beyond those waiting times, why wait when you can have your surgery abroad at a time that suits you and a surprisingly competitive price, carried out in state of the art facilities by highly reputable surgeons. A hip replacement in the United Kingdom can cost in the region of £10,000 if you don’t have private medical insurance. In the Ukraine, Kiev it can cost as little as £4300, that’s a huge saving.
The hips
The hip joint is one of the largest joints in the body.
In a healthy hip joint, the bones are connected to each other with bands of tissue known as ligaments. These ligaments are lubricated with fluid to reduce friction. Joints are also surrounded by a type of tissue called cartilage that is designed to help support the joints and prevent bones from rubbing against each other. The main purpose of the hip joints is to support the upper body when a person is standing, walking and running and to help with certain movements, such as bending and stretching.
Why do I need a hip replacement?
It might be necessary for you to have a hip replacement if one (or both) of the hip joints becomes damaged and causes you persistent pain or problems with everyday activities such as walking, driving and getting dressed.
Some common reasons why a hip joint can become damaged include:
osteoarthritis – so-called ‘wear and tear arthritis’, where the cartilage inside a hip joint becomes worn away, leading to the bones rubbing against each other rheumatoid arthritis – this is caused by the immune system (the body’s defence against infection) mistakenly attacking the lining of the joint, resulting in pain and stiffness, hip fracture – if a hip joint becomes severely damaged during a fall or similar accident it may be necessary to replace it.
Many of the conditions treated with a hip replacement are age-related so hip replacements are usually carried out in older adults aged between 60 to 80. However, in some cases a hip replacement may be necessary in children or younger adults whose hips do not develop in the right way (hip dysplasia).
The purpose of a new hip joint is to:
relieve pain improve the function of your hip improve your ability to move around improve your quality of life why a hip replacement may be necessary.
What happens during hip replacement surgery?
A hip replacement can be carried out under a general anaesthetic (where you are asleep during the procedure) or an epidural
(where the lower body is numbed).
(where the lower body is numbed).
The surgeon makes an incision into the hip, removes the damaged hip joint and then replaces it with an artificial joint that is a metal alloy or, in some cases, ceramic. The surgery usually takes around 60-90 minutes to complete.
An alternative to total hip replacement is hip resurfacing. This involves replacing the diseased or damaged surfaces in the hip joints with metal parts. This has the advantage of removing less bone so less prosthetic (implant) is needed.Recovering from hip replacement surgery
For the first four to six weeks after the operation you will be unable to place any weight on to your new hip so you will need a walking aid, such as crutches, to help support you.
You will also be enrolled on an exercise programme that is designed to help you regain and then improve the use of your new hip joint.
Most people are able to resume normal activities within two to three months but it can take up to a year before you experience the full benefits of your new hip.
What to expect after a hip replacement
Since its introduction in the 1960s, hip replacement surgery has proved to be one of the most effective types of surgery in modern medical history. Most people experience a significant reduction in pain and, to a lesser extent, improvement in their range of movement.
However, it is important to have realistic expectations about what the operation can achieve.
For example, you should be able to ride a bike but it is unlikely that you would be able to play a game of rugby safely (although as with most things, there are always exceptions to this rule).
The rehabilitation process after surgery can also be a demanding process and requires commitment.
Risks of hip replacement surgery
A modern artificial hip joint is designed to last for at least 20 years, but there is always the risk that the artificial hip joint can wear out or go wrong in some way before this time, meaning that further surgery is required to repair or replace the joint.
This is known as revision surgery. It is estimated that around 1 in 10 people with an artificial hip will require revision surgery at a later date.
There have been recent cases of metal-on-metal (MoM) replacements wearing quicker than would be expected, causing deterioration in the bone and tissue around the hip. There are also concerns that they could leak traces of metal into the bloodstream.
The risk of serious complications such as blood clots and infection at the site of the surgery is low; estimated to be less than 1 in a 100.
Alternatives
There is an alternative type of surgery to hip replacement known as hip resurfacing. This involves removing the damaged surfaces of the bones inside the hip joint and replacing them with a metal surface.
An advantage to this approach is that it is less invasive so has a faster recovery time and leaves you with a greater range of movement after surgery. However, it is usually only effective in younger adults who have relatively strong bones.
Read more about alternatives to hip replacements.
Future developments
Hip replacement surgery is being improved in several ways:
New, stronger materials for prosthetics are being developed that will allow longer wear and better joint mobility.
Enhancements are being made to new ‘cementless’ implants. Patients can be recommended for newer types of joints, such as ceramic-on-ceramic and ceramic-on-plastic.
Computer-assisted surgery is being used to generate an image of the hip joint to allow greater visibility and precision.
When a hip replacement is necessary
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis. It occurs when the joints become damaged over time and causes the surrounding cartilage to wear away. This causes the bones of the joint to rub together leading to hip pain stiffness and loss of movement. Osteoarthritis affects around 1 million people in England and Wales.
Rheumatoid arthritis.
In cases of rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system – which usually fights infection – attacks the cells that line the joints, making them swollen, stiff and painful. Over time, this can damage the joint itself, the cartilage and nearby bone.
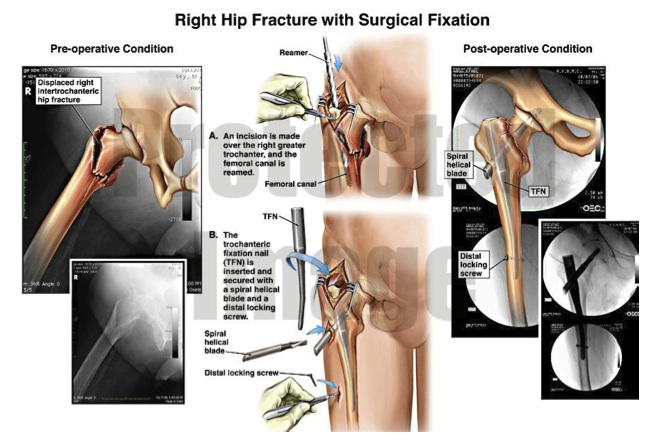
Hip fractures
Hip fractures are one of the most common causes of bone injury in older people, with an estimated 70,000-75,000 occurring each year in the UK. Most cases of hip fracture occur as a result of a fall.
It is possible to repair a fractured hip, but in some circumstances a hip replacement is recommended.
Less common causes of hip damage include:
septic arthritis – this form of arthritis occurs when the joint becomes infected
fracture of the neck of the thigh bone (femur) – this causes a loss of blood supply to the rounded head of the bone and may also lead to crumbling of the bone (avascular necrosis)
Paget’s disease of bone – this affects bone growth and can make bones weak and deformed bone tumours – abnormal cancerous growths that develop inside the bone hip dysplasia – which is where a baby is born with the bones in the hips being incorrectly aligned. Over time this misalignment can become worse, which sometimes means that it becomes necessary to replace the affected joint.